%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2
import sys
if '..' not in sys.path:
sys.path.append('..')
from ultrayolo import YoloV3, losses
from ultrayolo.datasets import CocoFormatDataset, common
from ultrayolo.helpers import draw
from pathlib import Path
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Yolo Loss Tutorial¶
The first create some random anchors and use the default masks
x = np.arange(5, 46, 5)
anchors = np.array(list(zip(x,x)), dtype=np.float32)
anchors[:,1] += np.random.randint(0, 10, 9)
anchors
array([[ 5., 14.],
[10., 16.],
[15., 21.],
[20., 21.],
[25., 26.],
[30., 39.],
[35., 41.],
[40., 45.],
[45., 47.]], dtype=float32)
masks = YoloV3.default_masks
masks
array([[6, 7, 8],
[3, 4, 5],
[0, 1, 2]])
And load the dataset using the SequenceDataset¶
filepath = Path('./toy_dataset/data_annotations_train.txt')
target_shape = (512, 512, 3)
batch_size = 2
is_training = True
max_objects = 10
train_seq = CocoFormatDataset('../minicoco_dataset/hair_drier_toaster_bear.json',
target_shape,
max_objects,
batch_size,
anchors,
masks,
base_grid_size=128,
is_training=is_training)
load coco annotations: 100%|██████████| 1714/1714 [00:00<00:00, 797895.34it/s]
train_seq.classes
[(23, 'bear'), (80, 'toaster'), (89, 'hair drier')]
Now we take a batch from the dataset¶
x_true, y_true_grids = train_seq[0]
The batch contains: - 2 images
x_true.shape
(2, 512, 512, 3)
3 grids
for i in range(len(y_true_grids)):
print(i, '-->', y_true_grids[i].shape, target_shape[0] / y_true_grids[i].shape[1])
0 --> (2, 4, 4, 3, 8) 128.0
1 --> (2, 8, 8, 3, 8) 64.0
2 --> (2, 16, 16, 3, 8) 32.0
The third value plotted represents the size in number of pixel of grid cells
Check that the dataset transformed is correct¶
for img_idx in range(len(x_true)):
print('Show annotations for image', img_idx)
img = x_true[img_idx]
for i in range(len(y_true_grids)):
y_data_grid_img = y_true_grids[i][img_idx]
ax = draw.show_img(img)
grid_len = y_data_grid_img.shape[1]
draw.grid(ax, img.shape[:2], grid_len)
grid_cell_size = target_shape[1] / grid_len
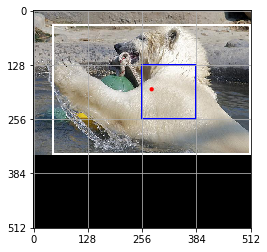
for grid_y, grid_x, box in np.argwhere(np.sum(y_data_grid_img[..., :4], axis=-1) > 0):
box_xyxy = (y_data_grid_img[grid_y,grid_x,box, :4] * target_shape[0]).astype(int)
class_id = np.argwhere(y_data_grid_img[grid_y,grid_x,box, 5:])[0][0]
draw.rect(ax, box_xyxy, 'white', 1)
print(y_data_grid_img[grid_y,grid_x,box, :4])
print(box_xyxy)
rect_resp = np.array([grid_x, grid_y]) * grid_cell_size
rect_resp = np.concatenate([rect_resp, rect_resp + grid_cell_size])
draw.rect(ax, rect_resp, 'blue', 2)
draw.point(ax, common.to_center_width_height(box_xyxy)[:2])
plt.show()
Show annotations for image 0
[0.86732817 0.36640626 0.9580156 0.45892185]
[444 187 490 234]
[0.8681094 0.48279685 0.9980469 0.6025 ]
[444 247 511 308]



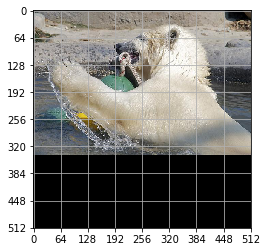
Show annotations for image 1
[0.09103125 0.06715625 0.9980469 0.65957814]
[ 46 34 511 337]
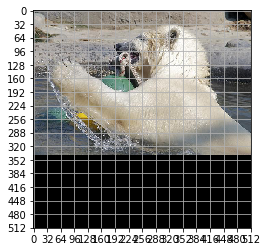
Create the model
model = YoloV3(target_shape, max_objects,
anchors=anchors, num_classes=train_seq.num_classes,
training=True, backbone='DarkNet', base_grid_size=128)
num pooling 2
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(model.model, show_shapes=True)
Evaluate how the loss works¶
We consider two cases:
when we got an initialized network the predictions should be around 0.5 (max entropy)
when we give as prediction the right labels the loss should be close to zero
y_pred_grids = model(x_true)
for y_pred in y_pred_grids:
print(y_pred.shape)
(2, 4, 4, 3, 8)
(2, 8, 8, 3, 8)
(2, 16, 16, 3, 8)
We take i=0 since all the images are in the first grid
i = 0
y_true = y_true_grids[i]
y_pred = y_pred_grids[i]
y_pred = tf.slice(y_pred, begin=[0,0,0,0,0], size=y_true.shape)
anchors_masks = anchors[masks[i]]
img_size = target_shape[0]
loss_fn = losses.make_loss(train_seq.num_classes, anchors, masks, img_size, len(train_seq))
ignore_threshold = 0.7
First Case¶
from ultrayolo.losses import YoloLoss
def to_box_xyxy(box_xy, box_wh, grid_size, anchors_masks):
"""convert the given boxes into the xy_min xy_max format
Arguments:
box_xy {tf.tensor} --
box_wh {tf,tensor} --
grid_size {float} -- the size of the grid used
anchors_masks {tf.tensor} -- the anchor masks
Returns:
tf.tensor -- the boxes
"""
# !!! grid[x][y] == (y, x)
grid = tf.meshgrid(tf.range(grid_size), tf.range(grid_size))
grid = tf.expand_dims(tf.stack(grid, axis=-1), axis=2) # [gx, gy, 1, 2]
grid = tf.cast(grid, tf.float32)
box_xy = (box_xy + grid) / tf.cast(grid_size, tf.float32)
box_wh = tf.exp(box_wh) * anchors_masks
box_wh = tf.where(tf.math.is_inf(box_wh), tf.zeros_like(box_wh), box_wh)
box_x1y1 = box_xy - box_wh / 2
box_x2y2 = box_xy + box_wh / 2
box_xyxy = tf.concat([box_x1y1, box_x2y2], axis=-1)
return box_xyxy
def process_predictions(y_pred, num_classes, anchors_masks):
"""process the predictions to transform from:
- pred_xy, pred_wh, pred_obj, pred_class
into
- box_xyxy, pred_obj, pred_class, pred_xywh
Arguments:
y_pred {tf.tensor} -- the predictions in the format
(NBATCH, x_center, y_center, width, heigth, obj, one_hot_classes)
num_classes {int} -- the number of classes
anchors_masks {tf.tensor} -- the anchors masks
Returns:
tuple -- box_xyxy, pred_obj, pred_class, pred_xywh
"""
# anchors_masks = tf.gather(anchors, masks)
pred_xy, pred_wh, pred_obj, pred_class = tf.split(y_pred,
(2, 2, 1, num_classes),
axis=-1)
pred_xy = tf.sigmoid(pred_xy)
pred_obj = tf.sigmoid(pred_obj)
pred_class = tf.sigmoid(pred_class)
pred_xywh = tf.concat((pred_xy, pred_wh), axis=-1)
grid_size = tf.shape(y_pred)[1]
box_xyxy = to_box_xyxy(pred_xy, pred_wh, grid_size, anchors_masks)
return box_xyxy, pred_obj, pred_class, pred_xywh
# 1. transform all pred outputs
# y_pred: (batch_size, grid, grid, anchors, (x, y, w, h, obj, ...cls))
anchors_masks_scaled = anchors_masks / img_size
pred_xyxy, pred_obj, pred_class, pred_xywh = process_predictions(
tf.cast(y_pred, tf.float32), train_seq.num_classes, anchors_masks_scaled
)
pred_xy = pred_xywh[..., 0:2]
pred_wh = pred_xywh[..., 2:4]
We expect that considering the variable pred_xywh the predictions
should be: - for xy in in average 0.5 - for wh close to 0 - for xy1, xy2
close to 0.5
While considering pred_xyxy it should be around 0.5
print('average xy', tf.reduce_mean(pred_xy))
print('average hw', tf.reduce_mean(pred_wh))
print('average xyxy', tf.reduce_mean(pred_xyxy))
average xy tf.Tensor(0.5, shape=(), dtype=float32)
average hw tf.Tensor(6.6419275e-09, shape=(), dtype=float32)
average xyxy tf.Tensor(0.5, shape=(), dtype=float32)
This is valid for all the objecteness and classes
print('average pred_obj', tf.reduce_mean(pred_obj))
print('average pred_class', tf.reduce_mean(pred_class))
average pred_obj tf.Tensor(0.5, shape=(), dtype=float32)
average pred_class tf.Tensor(0.5, shape=(), dtype=float32)
# 2. transform all true outputs
# y_true: (batch_size, grid, grid, anchors, (x, y, w, h, obj, ...cls))
true_box_xyxy, true_obj, true_class = tf.split(
y_true, (4, 1, train_seq.num_classes), axis=-1)
true_xy = (true_box_xyxy[..., 0:2] + true_box_xyxy[..., 2:4]) / 2
true_wh = true_box_xyxy[..., 2:4] - true_box_xyxy[..., 0:2]
box_loss_scale = 2 - true_wh[..., 0] * true_wh[..., 1]
inverting the pred box equations, to make it comparable with the transformations done for the predictions
grid_size = tf.shape(y_true)[1]
grid = tf.meshgrid(tf.range(grid_size), tf.range(grid_size))
grid = tf.expand_dims(tf.stack(grid, axis=-1), axis=2)
true_xy = true_xy * tf.cast(grid_size, tf.float32) - \
tf.cast(grid, tf.float32)
true_wh = tf.math.log(true_wh / anchors_masks_scaled)
true_wh = tf.where(tf.math.is_inf(true_wh),
tf.zeros_like(true_wh), true_wh)
The line 8 contains the opposite transformation made for the predictions
box_wh = tf.exp(box_wh) * anchors_masks
The masks are used to: 1. separate the boxes that contain objects and should be considered in the objects loss 2. from the boxes that not contain objects and should be considered in the no object loss
# 4. calculate all masks
obj_mask = tf.squeeze(true_obj, -1)
# ignore false positive when iou is over threshold
true_box_mask = tf.boolean_mask(
true_box_xyxy, tf.cast(obj_mask, tf.bool))
best_iou = tf.reduce_max(YoloLoss.broadcast_iou(
pred_xyxy, true_box_mask), axis=-1)
ignore_mask = tf.cast(best_iou < ignore_threshold, tf.float32)
Compute all the losses
xy, wh only with respect the objects that contains elements
xy_loss = obj_mask * box_loss_scale * \
tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(true_xy - pred_xy), axis=-1)
wh_loss = obj_mask * box_loss_scale * \
tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(true_wh - pred_wh), axis=-1)
the object and no object loss
You can check the whenever the loss is different to zero in the
obj_loss is zero in the no_obj_loss and vice-versa
obj_cross_entropy = tf.keras.metrics.binary_crossentropy(
true_obj, pred_obj, from_logits=False)
obj_loss = obj_mask * obj_cross_entropy
no_obj_loss = (1 - obj_mask) * ignore_mask * obj_cross_entropy
The class loss is computed only for the cells the contains objects
class_loss = obj_mask * tf.keras.metrics.binary_crossentropy(
true_class, pred_class, from_logits=False)
everything is reduced to one value per image
xy_loss = tf.reduce_sum(xy_loss, axis=(1, 2, 3))
wh_loss = tf.reduce_sum(wh_loss, axis=(1, 2, 3))
obj_loss = tf.reduce_sum(obj_loss, axis=(1, 2, 3))
no_obj_loss = tf.reduce_sum(no_obj_loss, axis=(1, 2, 3))
class_loss = tf.reduce_sum(class_loss, axis=(1, 2, 3))
loss = xy_loss + wh_loss + obj_loss + no_obj_loss + class_loss
loss
<tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=float32, numpy=array([35.51542, 47.17279], dtype=float32)>
Second Case¶
y_true == y_pred
i = 0
y_true = y_true_grids[i]
y_pred = y_true
Remember that y_pred is in format xy_min xy_max
pred_xyxy, pred_obj, pred_class = tf.split(
y_pred, (4, 1, train_seq.num_classes), axis=-1)
pred_xy = (pred_xyxy[..., 0:2] + pred_xyxy[..., 2:4]) / 2
pred_wh = pred_xyxy[..., 2:4] - pred_xyxy[..., 0:2]
pred_xywh = tf.concat((pred_xy, pred_wh), axis=-1)
true_box_xyxy, true_obj, true_class = tf.split(
y_true, (4, 1, train_seq.num_classes), axis=-1)
true_xy = (true_box_xyxy[..., 0:2] + true_box_xyxy[..., 2:4]) / 2
true_wh = true_box_xyxy[..., 2:4] - true_box_xyxy[..., 0:2]
box_loss_scale = 2 - true_wh[..., 0] * true_wh[..., 1]
# 4. calculate all masks
obj_mask = tf.squeeze(true_obj, -1)
# ignore false positive when iou is over threshold
true_box_mask = tf.boolean_mask(
true_box_xyxy, tf.cast(obj_mask, tf.bool))
best_iou = tf.reduce_max(YoloLoss.broadcast_iou(
pred_xyxy, true_box_mask), axis=-1)
ignore_mask = tf.cast(best_iou < ignore_threshold, tf.float32)
# 5. compute all the losses
xy_loss = obj_mask * box_loss_scale * \
tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(true_xy - pred_xy), axis=-1)
wh_loss = obj_mask * box_loss_scale * \
tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(true_wh - pred_wh), axis=-1)
obj_cross_entropy = tf.keras.metrics.binary_crossentropy(
true_obj, pred_obj, from_logits=False)
obj_loss = obj_mask * obj_cross_entropy
no_obj_loss = (1 - obj_mask) * ignore_mask * obj_cross_entropy
class_loss = obj_mask * tf.keras.metrics.binary_crossentropy(
true_class, pred_class, from_logits=False)
xy_loss = tf.reduce_sum(xy_loss, axis=(1, 2, 3))
wh_loss = tf.reduce_sum(wh_loss, axis=(1, 2, 3))
obj_loss = tf.reduce_sum(obj_loss, axis=(1, 2, 3))
no_obj_loss = tf.reduce_sum(no_obj_loss, axis=(1, 2, 3))
class_loss = tf.reduce_sum(class_loss, axis=(1, 2, 3))
loss = xy_loss + wh_loss + obj_loss + no_obj_loss + class_loss
loss
<tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=float32, numpy=array([0., 0.], dtype=float32)>
The loss is 0 when the prediction is equal to the true values
Conclusion¶
we have verified that the loss: - return max entropy value when the network is initialized, and - return 0 when the y_pred is equal to y_true